In the rapidly evolving field of machine learning, the need for continuous and automated quality assurance is becoming increasingly important. MLOps involves deploying, monitoring, and maintaining machine learning models in production, which requires strict adherence to quality standards. However, traditional point-in-time certifications fall short in providing trust in system that changes on a high pace. These certifications often lack timeliness and therefore stakeholder might not have trust in the systems the ability to proactively identify and address emerging risks and mitigations.
To meet the demanding requirements of MLOps IML4E has developed CABC for MLops.
What is it?
Continuous Auditing Based Certification (CABC) is a method for quality assessment and certification in dynamic systems, such as machine learning. It overcomes limitations of traditional point-in-time certifications by providing regular monitoring and analysis of data from the system to ensure compliance with standards and regulations. The CABC process involves evidence collection, assessment, and reporting. In a MLOps setup, CABC is implemented in two phases, with ongoing monitoring and automated assessment of artifacts generated during the ML lifecycle. The results of the assessments lead to the issuance or revocation of a certification.
More Information:
- “Towards a Risk-Based Continuous Auditing-Based Certification for Machine Learning”, Knoblauch, Dorian; Großmann, Jürgen
- “Towards Continuous Audit-based Cetification for MLOps”, Knoblauch, Dorian; Großmann, Jürgen
Contact

Dorian Knoblauch
Fraunhofer FOKUS
Phone +49 30 3463-7381
Send email
Why is it necessary?
ML deployments require strict adherence to quality standards. Traditional point-in-time certifications don’t require ongoing and automated quality assessment, which is the goto way of providing trust in a constantly changing system. Currently, audits are usually performed at intervals of 6 or 12 months, leaving a window of risk where no audit is performed. CABC enables organizations to proactively identify and address emerging risks, maintain the quality and reliability of their machine learning models, and ensure compliance with relevant standards and regulations through regular monitoring and analysis of data from the system.
How does it work?
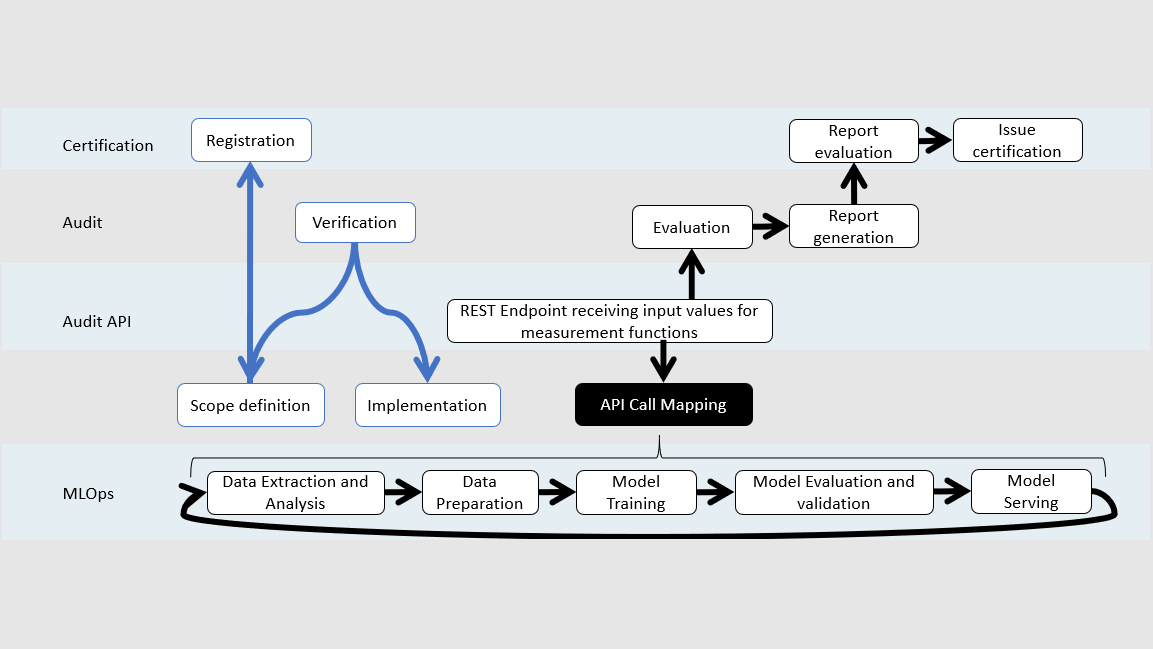
How CABC for MLOps is implemented
In the implementation of CABC for MLOps, risks for the ML system are first identified, and then quality requirements are specified and implemented. Measurements are performed on artifacts generated during the ML lifecycle. These artifacts include data sets, model architecture, model parameters, model performance metrics, model evaluation results, feature importances, model explanations, and model robustness. The assessments are continuously conducted, and the results are used to assess the compliance with the established quality requirements.
The evidence collection component involves the use of existing quality measurement tools, as well as specialized tools to automate the monitoring and collection of data from various sources within the ML pipeline. The collected data is then mapped to a unified API and delivered to the auditing entity, ensuring the independence of the assessment from the premises of the auditee. The assessment results are then transferred to the governing body, which either issues or revokes a certificate.
