VALICY – a virtual validation system for AI/ML and complex software applications
What is it?
VALICY is an AI based python framework that enables virtual validation for AI/ML (and also complex software) applications. It runs a multitude of AI instances to intelligently sample the testing space depending on several continuous or state-based input parameters of a classification problem. It is possible to predict several targets at the same time.
VALICY consists of:
- a relational data base (MySQL) as a data hub,
- a python framework to test black box applications that runs in docker containers on a dedicated server,
- a REST-API to communicate with VALICY, to provide test feedback and to get new test proposals for a black box application (AI of a customer)
- a front end for inspection of results, download of single runs for live testing and development of the certainty of result dimension(s)
More Information:
White Paper on Artificial Intelligence: a European approach to excellence and trust
Why is it necessary?
The European AI Act is a proposed set of regulations for artificial intelligence (AI) systems within the European Union (EU) that was introduced in April 2021. While it is not yet law, it is currently being reviewed by the European Parliament and the Council of the European Union. Some of the major agreements require a systematic virtual validation approach like VALICY applies. This is especially important for the section of the risk-based approach: The AI Act would categorize AI systems based on their potential risk level, with higher-risk systems facing stricter requirements. As VALICY is able to quantify the remaining uncertainty in the application range, this methodology will gain more and more interest, especially in safety-critical applications.
show moreValidating AI systems for safety-critical applications is a challenging task, as undetected areas of failure can lead to serious consequences such as harm to humans or expensive machinery. Some of the challenges of AI validation in safety-critical applications include:
1. Lack of comprehensive testing: AI systems can be extremely complex, and it can be challenging to test all possible scenarios and edge cases. There may be undetected areas of failure that only become apparent when the system is deployed in the real world.
2. Inability to account for all possible inputs: AI systems are designed to learn from data, but it can be difficult to account for all possible inputs that the system may encounter. This can lead to undetected errors when the system is deployed in the real world. To reduce the likelihood of such errors to a minimum, virtual validation is employed, therefore more tests can be performed, and the most critical parameter conditions can be identified for live testing. VALICY does that in an automated manner.
3. Limited understanding of the AI system’s decision-making process: In some cases, AI systems can be opaque or difficult to interpret, making it challenging to understand how the system arrived at its decisions. This can make it difficult to identify potential failure points or to validate the system’s performance. VALICY’s systematic approach to quickly identify the decision hyperplane tackles this issue.
4. Dynamic and evolving systems: AI systems can be dynamic and evolve over time, making it challenging to validate the system’s performance and to ensure that it continues to meet safety requirements over time.
To mitigate these challenges, it is important to use a combination of testing and validation methods, including black box and white box testing, formal verification, and simulation. VALICY focuses mainly on black box testing, as AI models are expensive to train, and companies are reluctant to reveal the core of their models. Additionally, it is important to design AI systems with safety in mind from the outset, and to involve domain experts in the design and validation process to ensure that the system meets the specific requirements of the application. Finally, it is critical to continually monitor the performance of the AI system and to update it as needed to ensure that it continues to meet safety requirements over time.
show lessHow does it work?
When an AI application is tested with VALICY, first, a job specification must be provided. This specifies the number of input dimensions together with corresponding minimum and maximum values, the number of target dimensions, a threshold, its nature (upper or lower), and a certainty target for each target dimension. All these dimensions could be provided in a scaled or normalized manner and named arbitrarily to disguise what is tested.
When a job is started first the regular grid is sampled, and the values are exported to the API to be validated by the application under test.
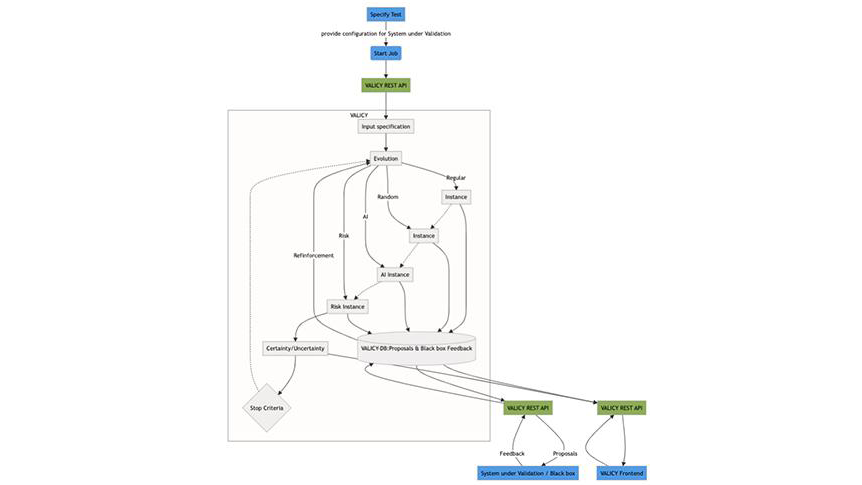
After all grid points are provided a result, the VALICY testing evolution starts with a set-up of competing AI configurations (along with some randomized parameter combinations) that obtain the evaluated points coming from the black box feedback runs. A VALICY job runs an evolution_controller (evolution box in figure) that spawns all the AI and other instances, manages data flow and training of corresponding job runs. At the moment, the pre-setting of competing instances is set from 3 up to 5. Depending on the problem under test, these values can be altered. A newly created AI instance always has a classification method (xgboost, randomForest, ANN) that will remain within a chain of evolution. E.g. if a XGBoost classifier is created, it will only be possible to pass an XGBoost configuration to its descendants. An instance will be fitted to all previously evaluated results. According to our hyperparameter variation setting in the box below, one can see which possibilities for a configuration are possible.
{“xgb”: [{“name”: “xgb_num_round”, “values”: list(range(10,100,10))},
{“name”: “max_depth”, “values”: list(range(2,11,1))},
{“name”: “learning_rate”, “values”: list(np.divide(range(1,101,9),100))},
{“name”: “objective”, “values”:[“binary:logistic”,”binary:hinge”,”binary:logitraw]}]}
We will constantly extend, evaluate and if reasonable, remove the degrees of freedom from the configurations.
A configuration can be AI based or random based. For an AI instance configuration VALICY has an internal evolutionary algorithm that can pass a successful configuration to its children. That means the Method of classification is always preserved during inheritance only hyperparameters are tuned. When a run is created (by an AI) all previously evaluated points are used as training set. New points that are proposed by an AI instance always try to identify points close to a decision boundary. VALICY also makes an internal guess what the black box feedback is assumed to be and takes this rating to determine if a configuration was successful, or not. The more successful the higher the scoring in VALICY. Every 10th run (a pre-set VALICY internal configuration parameter), a random or risk instance is started that arbitrarily places points within the test space. This serves two purposes, first to not get stuck once a transition of true/false is identified and secondly, that the points created by the AI instances are not biasing the certainty estimation result (AI results tend to be close to the decision hyperplane). A risk instance is estimating the achieved certainty by first placing samples in the under-sampled volumes applying a geometrical approach with inverted distances.
VALICY runs on dedicated servers in docker containers. If more nodes are needed, more cores can simply be added to the computational cluster. As the standard configuration is three instance runners and one evolution runner, the adding of nodes is performed in batches of 4 (, otherwise 1 evolution runner + number of instance runners per evolution runner).
For inspection of results, a front end allows to inspect the results, see the distribution of test proposals along with the evaluated results, and gain some insights. This is a work in progress, we regularly update it, when new features become available.
To monitor the operation of VALICY, Grafana dashboards are used.
The VALICY customer communication always uses the VALICY Rest API for a standardized and secure communication. After full virtual validation run, the resulting certainty is available along with all the run results.
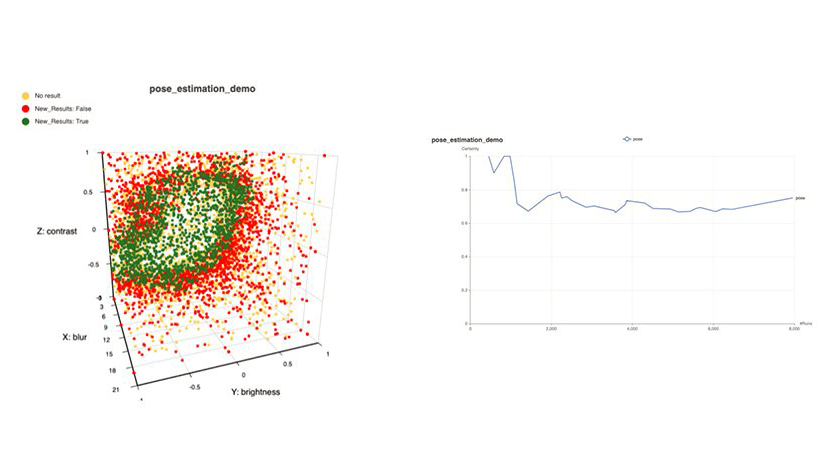
Lately, we added clustering of the results for both True and False points. Clustering is done applying Gaussian Mixture Models (default), but kmeans can also be used. For the clusters we also provide characteristics like, number of points per cluster, volume (multidimensional), fraction of points on the outer silhouette, clusters with an overlap and its percentage, outliers of the clusters etc.